The word “tissue” is often used to describe the various types of material that form part of our bodies. It can refer to any type of living material found in humans, animals, or plants. Our organs and tissues are made up of cells, which are very small units that carry out specific functions within our body.
You may wonder why we need tissue studies. There is a lot of information to learn when you go into medical school. However, the main purpose of the subject is to help us understand how things work in the human body. We can also use tissue research to diagnose and treat diseases.
This way, students can choose their topic for the study of tissue. They might consider something like muscle, brain, skin, blood, or cartilage, among others. Whatever they choose, this will allow them to gain knowledge about a particular organ or tissue.
In addition to knowing more about the structure of an individual’s body, students should be able to know how these different parts function as well.
A Brief History of the Study of Tissue
Tissues can be found throughout your body. For example, you have skin, fat, muscle, bone, blood, cartilage, nerves, tendons, ligaments, and more.
When you look at a piece of paper, it seems like all that matters is the ink. However, the truth is that tissues are very important. If you want to understand how they work, then you need to learn about the history of the study of these kinds of materials.
You might ask why someone would want to know about this. Well, for one thing, it can help doctors diagnose diseases and injuries. It also helps them figure out what treatments will work best for patients. And finally, it allows researchers to create new medicines.
For scientists to learn about how tissues function, they first had to find ways to preserve them. Back in ancient times, people used to store their dead bodies by placing them in jars. As time went on, people began to use other methods.
For instance, early Egyptians preserved the brain with honey and later used resin.
What Are Tissues?
Tissues are the basic building blocks of the human body. Without them, you wouldn’t be able to survive. Your skin, your bones, your muscles, and everything else that makes you who you are would all have to come from somewhere. So where does it all go?
This is a very complicated question, but we’re here to help you understand the basics. The first thing you need to know is that your tissues aren’t just made up of cells. There are also proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and other substances in each tissue.
Your organs are the most important parts of the body. They take care of almost every aspect of your life. For example, the liver takes care of your blood, the kidneys cleanse your blood, and the lungs keep you alive by breathing air into your system.
The heart is a muscle that pumps blood throughout the entire body. It’s also responsible for keeping your body temperature regulated.
The brain is the control center of the body. You can think about it as being like a computer, except that it doesn’t run on electricity. Instead, it runs off chemicals.
Tissue: How It Works
Tissues can be used for many different purposes. For example, tissues are commonly used when people need to clean their ears or noses. Some tissues help you to keep your hands warm. This article will explain exactly what tissue is and why it’s so important to know how it works.
You might have heard of the term “tissue” before, but you probably didn’t realize just how useful it can be. When you’re talking about tissue, you mean a type of paper product. The word comes from the Latin words tissues and tabula.
These two terms were combined to create the English language word, tissue. Tissue is made up of fibers that are bound together by glue. You’ll find these products in bathrooms, kitchens, and bedrooms all around the world.
The first thing you should know is that tissues aren’t very strong. They can tear easily, especially if you use them to wipe your nose or mouth. But they are great at absorbing moisture. If you want to learn more about what tissues are, then you should read this article.
Why do people need tissues? Because they absorb liquid. If you put a tissue in a bowl of water, then it will become soggy because it has absorbed the liquid.
Why Is Tissue Important?
Tissues are essential for life. Without them, we would be unable to survive. This includes things like skin, muscle, bone, fat, blood, etc. For example, without bones, your body wouldn’t have any structure.
As you might imagine, tissues come in many different shapes and sizes. There are also several different kinds of tissues. Some examples include connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscular tissue, nervous tissue, and vascular tissue.
This article will focus on the function of one type of tissue, namely, the epidermal layer of cells that covers the outer surface of our bodies.
Epithelia line the inside and outside of all of the organs in the human body. The most common kind of epithelium is the skin. When we refer to the “skin” it usually means the topmost layer of the epidermis. It’s made up of a single layer of flat, squamous, non-keratinized cells, and is composed of two main parts.
The first is the stratum corneum, which is the uppermost layer of dead, keratinized cells. Underneath this are living layers of basal, spinous, granular, and cornified (or horny) cells.
What Are the Different Types of Tissue?
Tissues are made up of cells. There are three main categories of tissues: connective, epithelial, and muscle. Connective tissues make up most of your body. Epithelial tissues line your organs and glands. Muscle is found inside the muscles.
Connective tissues are used to hold structures together. For example, bones are held together by connective tissue. The skin and mucous membranes are also made up of connective tissue.
Epithelial tissues protect organs from damage, and they help them to function properly. Examples of epithelial tissues include the lining of the stomach, intestines, lungs, and bladder.
Muscle is a type of tissue that makes up your skeletal system, including the muscles in your arms and legs. Muscles contract, allowing you to move.
What Are the Different Types of Tissue?
The different types of tissue are important when it comes to understanding how the human body works. You should know that each part of your body contains a specific combination of these three types of tissues.
For instance, bone is primarily composed of calcium, while cartilage is mainly made of collagen.
What Is the Study of Tissue Known As?
Histology is a discipline of science concerned with the study of various tissues and their structures. The structure of every single tissue in the human body is linked to its various functions. As a result, histology is intimately linked to both physiology and anatomy.
Tissues can be found in almost any part of your body. For example, skin, bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, blood vessels, lymph nodes, nerves, glands, and organs all contain tissues.
In addition to being a major component of the human body, tissues also have many functions. One of these functions is to help support the body’s various parts. Another important function of tissues is to protect other structures within the body.
While some tissues are very obvious, others are harder to notice. Some examples of this include fat cells, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
What is a Study of Tissue? The word “tissue” comes from two Latin words: tissue meaning “body”, and lignum meaning “wood”. This means that the word “tissue” literally translates into “the wood of the body.”
The study of tissues is one of the most interesting topics in biology. It involves anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, histology, embryology, pathology, and microbiology.
Why Is Studying About Tissue Important?
If you’re looking to get into medical school, you’ll need to know all of the information that you can. And one of the most important things that you should learn is how human cells work. This is why you should study the topic of tissue.
Tissues are the basic building blocks of the body. The main function of tissues is to provide support and protection to organs. For example, your skin protects you from the elements, and your bones protect your internal organs.
There are four different kinds of tissues in the body: connective, epithelial, muscle, and nervous. Each type of tissue plays an essential role in the overall health of your body.
When you’re learning more about these different types of tissues, you’ll be able to understand what goes on inside the human body.
This will also help you when it comes to understanding the causes of disease. So, if you want to make sure that your future career involves helping people, then you need to start studying tissue.
What Are the Functions of Tissue?
Tissues help to protect your body against damage from outside sources. When you cut yourself, tissues will start to repair the wound so that it doesn’t get infected. If you have an injury, then this is when the tissue begins to heal. This process usually takes a few days.
If you’re injured, then you’ll need to replace the damaged cells with new ones. This requires the growth of new blood vessels. The purpose of these blood vessels is to provide nutrients and oxygen to the area where the cell was destroyed.
When you die, all of the dead cells are removed by scavengers. Scavenger cells also clean up waste products. However, if there’s not enough space for the new cells to grow, then your body may produce more cells than it needs.
In addition to cleaning up after you’ve died, the skin helps to keep you warm and dry.
The mucous membranes line your digestive tract. They allow food particles to pass through while preventing bacteria from entering the bloodstream.
The connective tissues hold organs together. They help to prevent internal injuries.
The nervous system is made of neurons that transmit messages throughout the body.
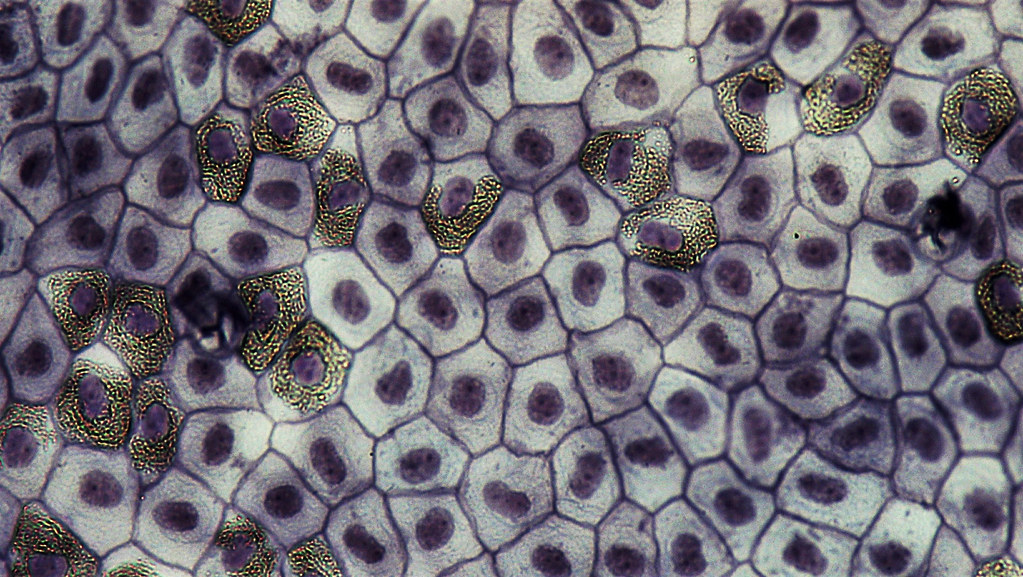
Who Studies Tissues?
Who studied the tissue?
-Tissue study is very important in the field of biology. The research on the tissue can help us to understand the body more deeply. And the results of the research will be used to treat the disease.
What’s the most important thing that you need to know?
1. The first step for studying the tissue is to collect samples from the patients.
2. After collecting the sample, the scientists use the microscope to observe the cells under the light.
3. Finally, the researchers analyze the data and write their papers.
How many people are involved in the study?
There are lots of different people who participate in the research. For example, the doctor, the nurse, the technician, and the students.
Why do we have to learn about the tissue?
Because the human being is the most complicated system. There is no doubt that the tissues of the human body can’t work alone. So, it needs the help of other parts. To understand the function of the tissue, we should know about its structure.
What does a scientist do when they study the tissue?
Scientists use a variety of techniques to study the tissue. For instance, they may perform a biopsy, or take some blood samples.
Why Should Pathologists Study Tissues?
There are many reasons why a doctor needs to examine tissue samples. The first thing that you need to know is that the medical field uses different methods to diagnose patients. Doctors use various tests to determine whether someone has cancer, heart disease, diabetes, or any other condition.
Tests like blood work, X-rays, and CT scans help doctors figure out the health issues of their patients. However, these procedures don’t always give them all of the information that they need to make an accurate diagnosis. This is where the use of biopsies comes into play.
A biopsy is a procedure that involves taking a sample of cells or tissue from a patient’s body. A pathologist examines the results of the test and makes a final decision based on what he sees. If the lab techs are unable to identify the problem, then they will send the sample to another lab to be examined by a specialist.
To do this, the technician takes the sample out of the body, cleans it, fixes it, embeds it in paraffin wax, slices it, stains it, covers it with glass, cuts it, slides it, and finally reads it under a microscope.
