Lumen is a unit of measurement that describes how much light travels a distance in a given amount of time. It can also be defined as the smallest possible segment of light and is measured in micrometers (µm). The name “lumen” comes from the Latin word Luminus, meaning “light”.
In biology, lumen refers to the space within a cell occupied by the cytoplasm, the contents of a cellular organelle. Larger cells contain more lumens than smaller ones do; for example, red blood corpuscles have many times the number of lumens found in white blood corpuscles.
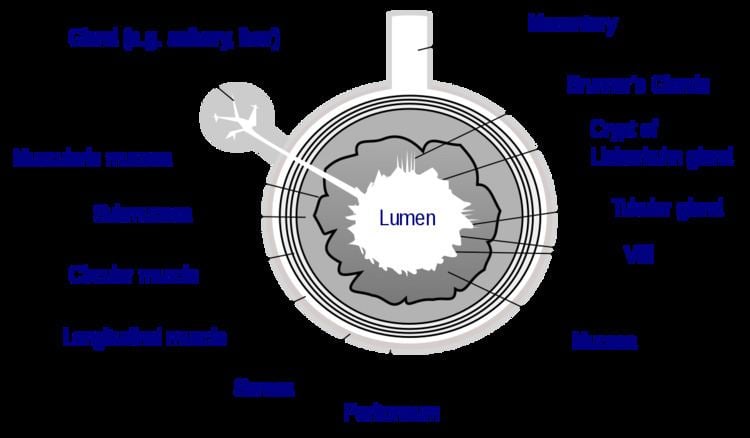
The luminal surface of epithelial tissue lines organs such as the stomach, intestine, bladder, kidney, lung, uterus, ovary, and Fallopian tube.
It has been proposed that lumen formation may play an important role during development. For instance, the formation of the eye lens requires the ingrowth of a mass of fibers into the center of the ocular globe.
Why It Is Necessary to Know About Lumen for Biology Students?
If you’re studying biology, then you need to understand how light works to be able to answer questions correctly. You’ll also want to have a basic understanding of the different parts that make up the human eye. This will help you to gain an insight into the various functions of the body.
In this article, we’ve explained why it’s important to learn about the function of the lens of the eye when you study biology. We hope that you now feel better equipped with the knowledge you need to succeed in your studies.
To get started, you should look at the diagram below. The first thing to notice is that the iris and the cornea are both transparent. However, they work together to protect the retina.
You can then move on to the next section. Here, you’ll find a picture of the eyeball. If you look closely, you’ll see that there is another small structure inside the eyeball. This is the pupil. It controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Next, take a look at the image of the lens. You’ll see that it is surrounded by a membrane called the capsule. Inside, there are two layers.
The outer layer contains cells that produce proteins. These proteins are responsible for holding onto the water to keep the lens soft and pliable.
What Is the Lumen of a Cell?
A lumen is a very small opening that allows light to enter a body. The word “lumen” comes from Latin, meaning “light.” So, what does this have to do with biology? Well, when you look at cells, you’ll notice that they contain tiny openings. This is where the lumen of the cell is located.
When scientists talk about the size of these openings, they use a measurement known as the diameter. For example, the diameter of a red blood cell is around 7 micrometers. In other words, it’s approximately one-thousandth of an inch. You may also know that the human eye can focus on objects that are no more than 20/20 vision, which means that you can see things that are less than 0.5 millimeters away.
So how big is a cell? If you want to find out, you should take a close look at your microscope. When you’re looking through the lens, you’ll be able to measure the distance between two points. Then, divide this number by 2 and multiply it by pi. Pi stands for 3.
How Does the Lumen Work?
A lumen is a structure found inside many animals. It helps to regulate how much light enters their eyes so that they can see better. Lumens have a lot of similarities to human eye structures, but there are also differences.
In humans, the cornea reflects incoming sunlight onto the retina. The iris controls the amount of light entering the eye. If the pupil becomes smaller, less light will enter the eye.
Inside the eye, there are two chambers: the anterior chamber and the posterior chamber. In the front part of the eye, the cornea is attached to the sclera. This is the white of the eye. Behind the cornea is the aqueous humor.
When the aqueous humor moves through the lens into the vitreous body, it pushes against the vitreous gel. In the back of the eye, the fluid flows from the vitreous body to the choroid and then to the ciliary body.
The choroidal blood vessels are very close to the retinal pigment epithelium. When a person blinks, this movement causes a pressure change in these blood vessels.
What Are the Functions of the Lumen?
When you’re studying biology, one of the most important things that you need to know is how a cell works. You can use the information below to help you understand how cells work.
A lumen is a small tube within a larger structure. For example, when you look at an animal, you’ll notice that there are many different kinds of tubes and cavities.
These structures allow the body to function properly. There’s also a lot of movement in these parts of the body, so it makes sense that the body would have lots of little holes or openings.
For the body to be able to move, it needs to create a network of tubes and channels. This is why the lumen is such a vital part of the human body.
If you want to learn more about the lumen, then you should check out the article below. It will give you some great tips on what you can do to improve your health.
The first thing that you should realize is that there are two main types of lumens. The first type is a hollow tube. These tubes are found in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other organisms.
The second kind of lumen is a solid cylinder. These are often used for transporting food through the digestive system.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-590279623-56b6225d5f9b5829f830c85e.jpg)
What Are the Benefits of Lumen?
In biology, lumens are usually found in organs like the stomach, small intestine, colon, large intestine, gallbladder, uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, cervix, urethra, nose, ear, eyes, etc. Lumen refers to the space inside an organ that is used for digestion, absorption, excretion, storage, secretion, circulation, and transport of fluids and solids.
A lumen can be seen as a tube-like opening in the wall of an organ or tissue. The word “lumen” comes from the Latin meaning “light.” When we look at the anatomy of the body, it’s easy to understand why this is the case. In most cases, the walls of these structures are thin and translucent.
There are many different types of lumens in the human body. For example, there are blood vessels that carry blood throughout our bodies. There are also lymphatic channels, which drain fluid away from tissues.
When we talk about the digestive system, we’re talking about all of the organs involved with food processing. This includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus, liver, pancreas, gall bladder, spleen, appendix, and so on.
How to Use Lumen in Biology
In this article, I will tell you how to use the lumen in biology. Lumen is a very important part of your life. If you don’t know how to use it correctly, you can get hurt. So, you should learn to be careful when using lumens. You need to understand the rules so that you can avoid getting injured.
When you go to school, you will meet many people who are studying different subjects. For example, you might have a friend who studies chemistry. Or you may have someone else who likes to study physics. As soon as they start their classes, you’ll notice that they always seem to carry around a small flashlight with them. This is because they need to be able to read the material in front of them at night.
Now, you might ask why you would want to do this. After all, you can just turn on your reading light. The answer is that you need to use a special type of lighting known as a lumen.
If you’re wondering what lumen does, then I’m going to explain it to you here. Lumen is the name given to any type of light source. When you use a lumen, you are shining light onto whatever surface you are working on.